5 Fleas of animals
Last modified on 02. January 2026 at 20:35:10
“A quote.” — Dan Meyer
5.1 General background
What is a data grid?
5.2 Theoretical background
5.3 R packages used
R Code [show / hide]
pacman::p_load(tidyverse, conflicted)5.4 Data
Small data and grid
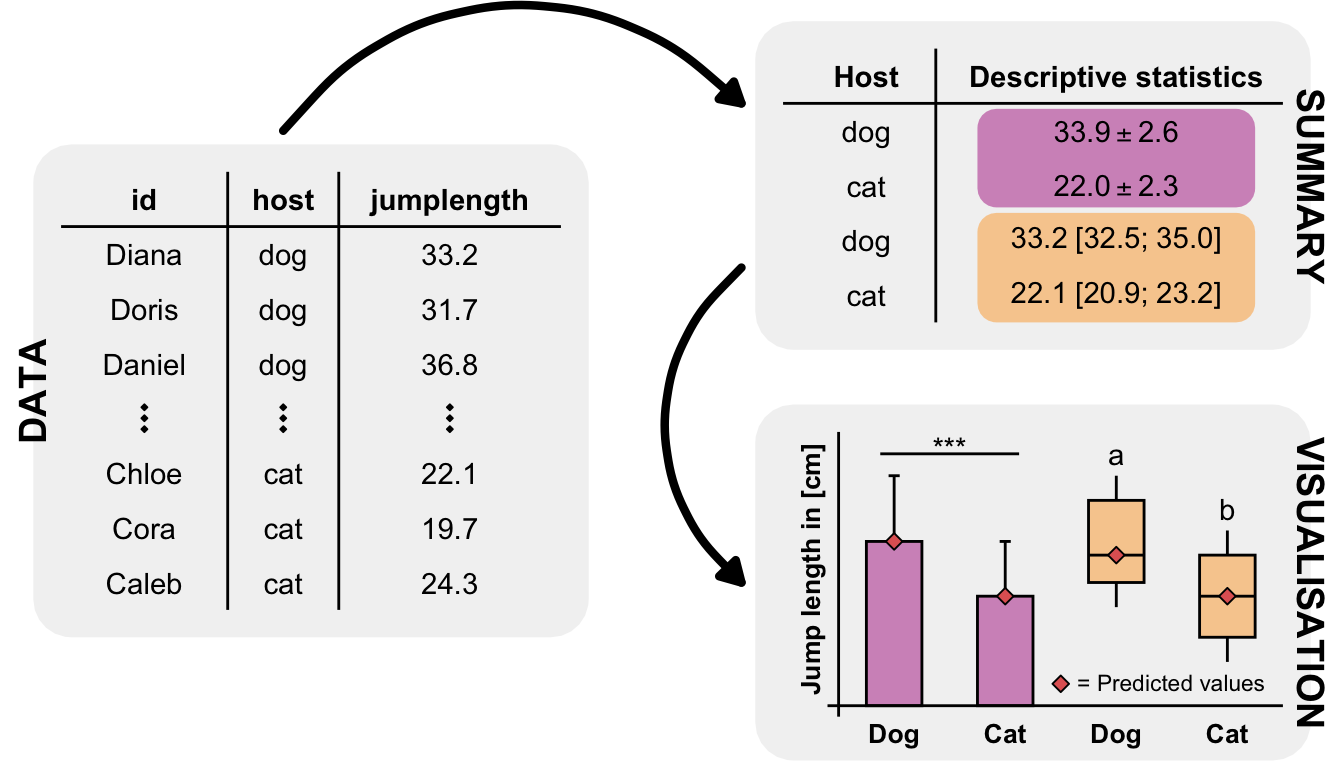
5.4.1 Jump performances of fleas
C. felis felis jump was \(19.9 \pm 9.1cm\) with a range from \(2\) to \(48cm\)
C. canis jump was longer \(30.4 \pm 9.1cm\) with a range from \(3\) to \(50cm\)
R Code [show / hide]
jump_flea_grid <- expand_grid(host = c("cat", "dog")) |>
mutate(mean = c(19.9, 30.4),
sd = c(9.1))R Code [show / hide]
jump_flea_tbl <- jump_flea_grid |>
rowwise() |>
mutate(jumplength = lst(rnorm(7, mean, sd))) |>
unnest(cols = jumplength) |>
mutate(host = as_factor(host))R Code [show / hide]
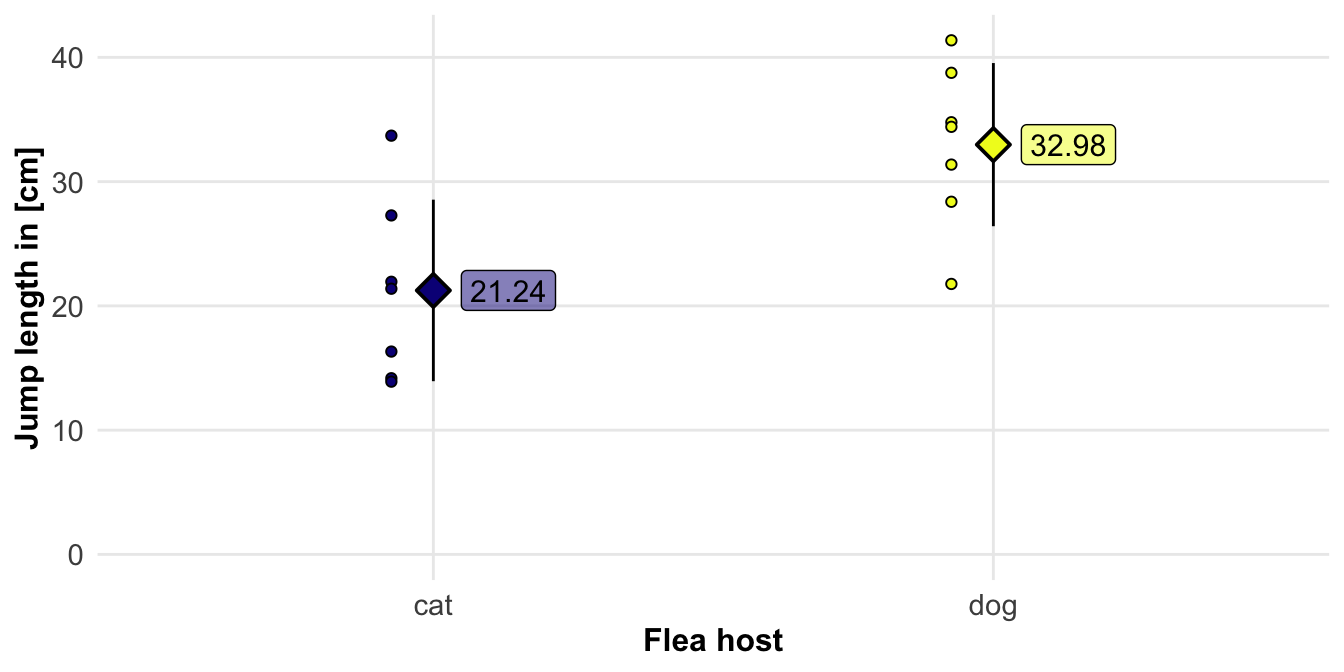
jump_flea_tbl |>
group_by(host) |>
summarise(mean(jumplength),
sd(jumplength)) |>
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, 2)# A tibble: 2 × 3
host `mean(jumplength)` `sd(jumplength)`
<fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 cat 21.2 7.3
2 dog 33.0 6.57R Code [show / hide]
jump_animals_grid <- expand_grid(host = c("cat", "fox", "rat", "dog")) |>
mutate(mean = c(19.9, 35.2, 15.2, 30.4),
sd = c(9.1, 10.3, 4.6, 9.1))R Code [show / hide]
jump_animals_tbl <- jump_animals_grid |>
rowwise() |>
mutate(jumplength = lst(rnorm(7, mean, sd))) |>
unnest(cols = jumplength) |>
mutate(host = as_factor(host))R Code [show / hide]
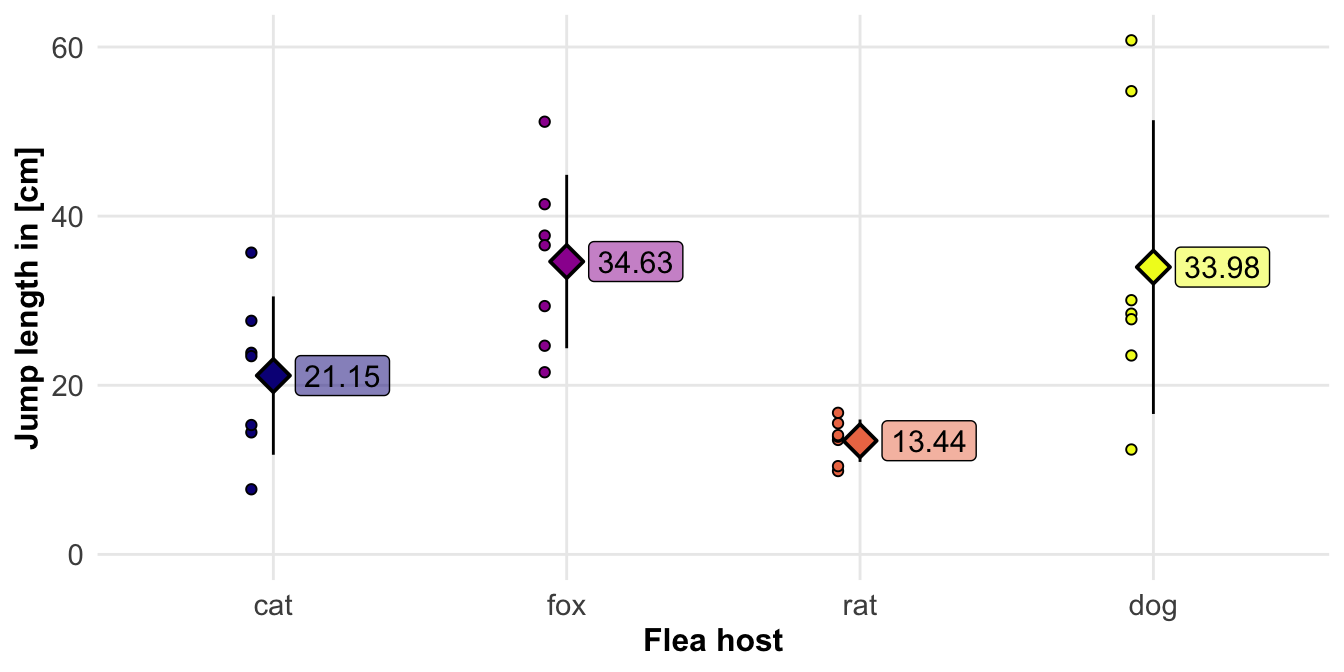
jump_animals_tbl |>
group_by(host) |>
summarise(mean(jumplength),
sd(jumplength)) |>
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, 2)# A tibble: 4 × 3
host `mean(jumplength)` `sd(jumplength)`
<fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 cat 21.2 9.36
2 fox 34.6 10.2
3 rat 13.4 2.51
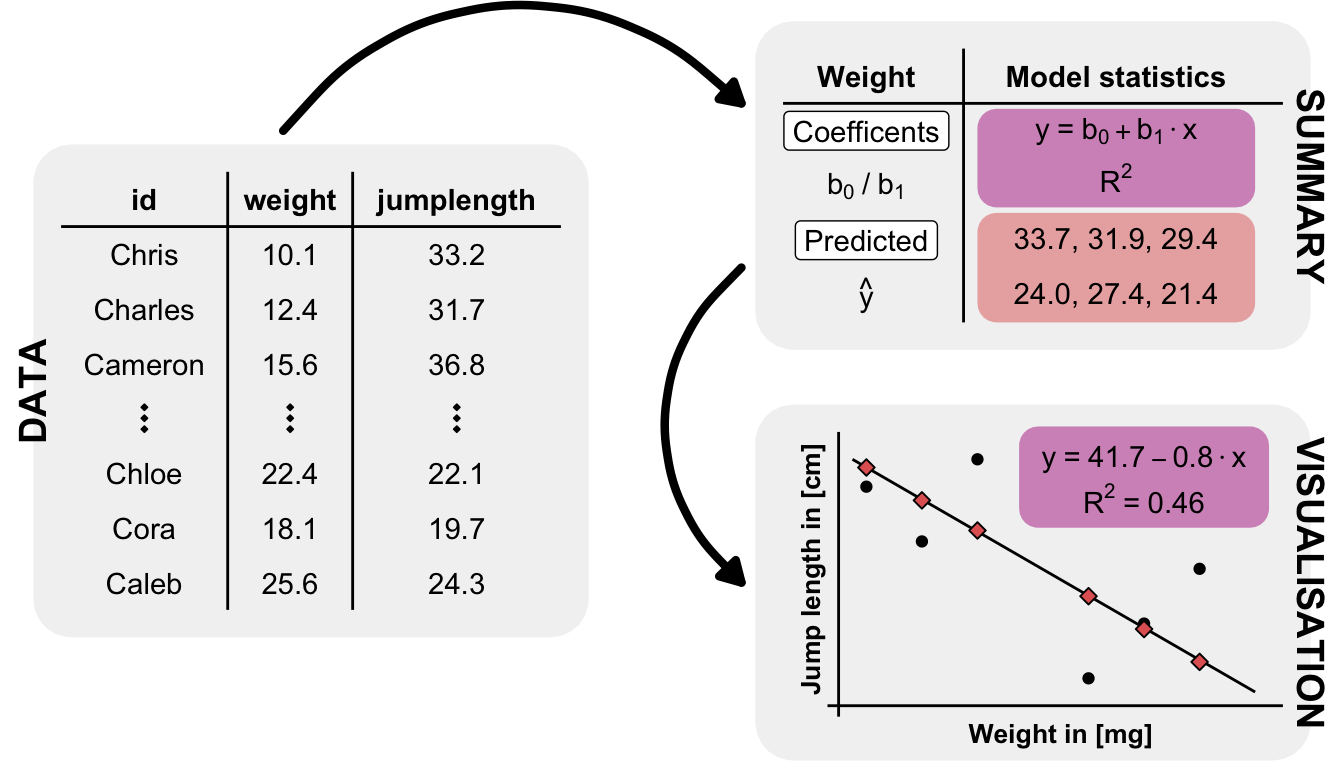
4 dog 34.0 17.4 5.4.2 Measurements on animal fleas
- Jump length in [cm] called
jump_length - Number of hairs on each leg called
count_leg_leftandcount_leg_right - Ratings of each flea, as listed in the catalog of the Fédération Internationale de la Beauté des Puces (FIBP) called
ratingon a Likert scale from 1 to 5, with 5 being the strongest expression. - The infection status with the flea cold is called
infected, with a value of 0/1 for no/yes.
R Code [show / hide]
tibble(jumplength = rnorm(7, 5, 1),
counthairleg_left = rpois(7, 4),
counthairleg_right = rpois(7, 4),
counthairleg = (counthairleg_left + counthairleg_right)/2,
rating = sample(1:5, 7, replace = TRUE, prob = c(0.1, 0.2, 0.4, 0.2, 0.1)),
infectd = rbinom(7, prob = 0.5, size = 1))# A tibble: 7 × 6
jumplength counthairleg_left counthairleg_right counthairleg rating infectd
<dbl> <int> <int> <dbl> <int> <int>
1 6.17 4 8 6 3 1
2 5.03 5 5 5 4 0
3 6.51 6 1 3.5 3 0
4 4.38 2 1 1.5 3 1
5 2.62 0 3 1.5 3 0
6 6.64 3 3 3 2 0
7 3.82 3 3 3 3 05.4.3 Fleas in urban and rural habitats
Why so complex?
R Code [show / hide]
jump_habitat_grid <- expand_grid(host = 1:3, site = 1:2) |>
mutate(mean_host = c(19.9, 19.9, 30.4, 30.4, 15.2, 15.2),
mean_site = c(5, 0, 5, 0, 5, -5),
mean = mean_host + mean_site,
sd = c(9.1, 9.1, 9.1, 9.1, 4.6, 4.6))
jump_habitat_grid# A tibble: 6 × 6
host site mean_host mean_site mean sd
<int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1 1 19.9 5 24.9 9.1
2 1 2 19.9 0 19.9 9.1
3 2 1 30.4 5 35.4 9.1
4 2 2 30.4 0 30.4 9.1
5 3 1 15.2 5 20.2 4.6
6 3 2 15.2 -5 10.2 4.6R Code [show / hide]
jump_habitat_raw_tbl <- jump_habitat_grid |>
rowwise() |>
mutate(jumplength = lst(rnorm(7, mean, sd))) |>
unnest(cols = jumplength)R Code [show / hide]
jump_habitat_tbl <- jump_habitat_raw_tbl |>
select(host, site, jumplength) |>
mutate(host = factor(host, labels = c("cat", "dog", "rat")),
site = factor(site, labels = c("urban", "rural"))) |>
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, 2)R Code [show / hide]
jump_habitat_tbl |>
group_by(host, site) |>
summarise(mean(jumplength),
sd(jumplength)) |>
mutate_if(is.numeric, round, 2)# A tibble: 6 × 4
# Groups: host [3]
host site `mean(jumplength)` `sd(jumplength)`
<fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl>
1 cat urban 21.8 9.26
2 cat rural 23.6 7.23
3 dog urban 35.2 9.1
4 dog rural 27.9 12.8
5 rat urban 19.2 1.85
6 rat rural 12.8 3.745.5 Data availability
The data is available as txt-Files under https://github.com/jkruppa/biodatascience.
5.6 Alternatives
Further tutorials and R packages on XXX
5.6.1 Why linear is a bad idea?
R Code [show / hide]
jump_flea_tbl <- tibble(host = rep(0:1, each = 7),
jump_length = 19.9 + 10.5 * host + rnorm(14, 0, 9.1)) |>
mutate(host = factor(host, labels = c("cat", "dog")))5.6.2 Why is a tibble() bad idea?
R Code [show / hide]
jump_animals_tbl <- tibble(cat = rnorm(n = 7, mean = 19.9, sd = 9.1),
fox = rnorm(n = 7, mean = 35.2, sd = 10.3),
rat = rnorm(n = 7, mean = 15.2, sd = 4.6),
dog = rnorm(n = 7, mean = 30.4, sd = 9.1)) |>
pivot_longer(cols = cat:dog, values_to = "jump_length", names_to = "host") |>
mutate(host = as_factor(host))5.7 Glossary
- term
-
what does it mean.
5.8 The meaning of “Models of Reality” in this chapter.
- itemize with max. 5-6 words
5.9 Summary
References
[1]
Wickham H, Çetinkaya-Rundel M, Grolemund G. R for Data Science: Import, Tidy, Transform, Visualize, and Model Data. " O’Reilly Media, Inc."; 2023.
[2]
Cadiergues MC, Joubert C, Franc M. A comparison of jump performances of the dog flea, ctenocephalides canis (curtis, 1826) and the cat flea, ctenocephalides felis felis (bouché, 1835). Veterinary parasitology. 2000;92(3):239-241.
[3]
Wickham H, Henry L. Purrr: Functional Programming Tools.; 2025. https://purrr.tidyverse.org/