3 What is a model?
Last modified on 12. February 2026 at 08:18:51
“Space: the final frontier. These are the voyages of the starship Enterprise. Its continuing mission: to explore strange new worlds; to seek out new life and new civilizations; to boldly go where no one has gone before!” — Star Trek: The Next Generation, intro
“Is this limestone?” Emma asked, looking through the narrow window in the castle wall. She pushed the wall slightly with her hand. It was massive and stable.
“No, it’s plastic. Pure plastic,” Jeff answered from the darkness. “But it feels real. Sometimes your senses tricked you.”
Emma leaned over the wall. “The stones are perfect squares in the basement, but they’re getting smaller here in the walkway, like tiny dice,” Emma wondered.
“It’s the optimum. The optimum.” Jeff spoke quietly.
She moved to the opposite side of the wall where the battlement walk was located. The castle was meant to be situated near Prague in Old Europe. The play was to concern the drama between Tycho Brahe and Nicolaus Copernicus. She wondered who would play them, but another question came to her mind first.
“Why is it dark at night, Jeff?”
There was a long pause of silence and breathing. “Because the universe is expanding. The light is stretched out. The wavelength became longer and longer until the light could no longer be seen,” Jeff answered in a stoic undertone.
Emma looked surprised. “Yesterday, I explained the issue with a stick, an orange, and a flashlight.”
A pause of silence followed. “Your model was wrong,” Jeff stated.
“It was useful and a lot of fun,” Emma answered, sounding annoyed. Her view was captured by the castle’s long walls, which stretched away like curved lines.
Imagine you are standing on a globe but still believe it is flat. This globe is called Earth. It is your home planet. So far, you know that you belong to the only existing intelligent species. You are standing on solid ground, with boiling rocks just a few kilometers below you. If you shrink the Earth to the size of an egg, the shell would represent the solid ground. A few kilometers above that, you would not be able to breathe. You are not moving right now, but the Earth is moving at speeds of up to 828,000 km/h depending on the reference point. Your reality is a serious misinterpretation. This chapter focuses on the important role of different models of reality. We will examine various historical examples of scientific work by humans. Theories were developed and predictions were made. Most of these predictions were incorrect. Only a few provided a satisfactory explanation of the reality we live in. We want to follow the historical paths and go where no one has gone before.
%% rewrite David Deutsch: “To interpret dots in the sky as white-hot, million-kilometre spheres, one must first have thought of the idea of such spheres. And then one must explain why they look small and cold and seem to move in lockstep around us and do not fall down. Such ideas do not create themselves, nor can they be mechanically derived from anything: they have to be guessed – after which they can be criticized and tested.”1
%% What is real?
Sometimes we need a model to know what is real.
%%
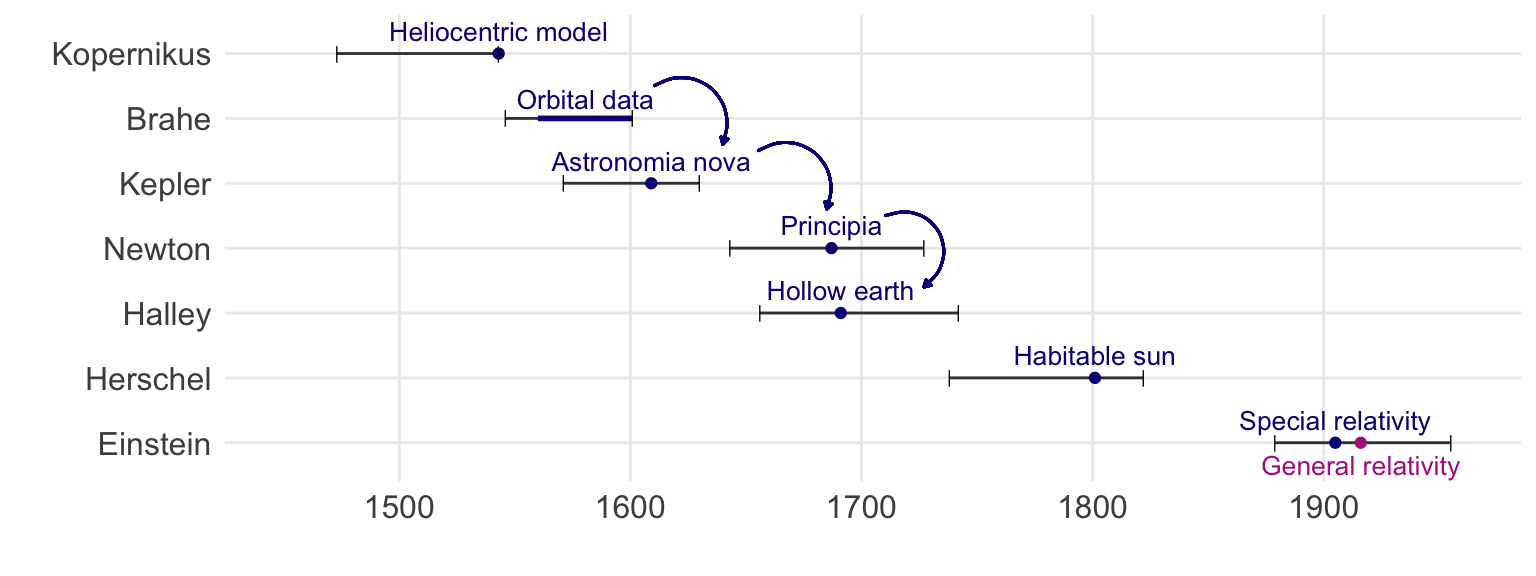
Who are these humans, and what is their background? What have they achieved? The science in books loses its humanity. I am in your head, talking to you. You read about the achievements of men who created beautiful things. They had ideas that came out of nowhere. More or less, that’s how it seems. But they were human, and therefore interconnected with other people of their time. Or with the knowledge of their ancestors. I think it’s important to understand these connections in order to gain a better understanding of the theories scientists propose and how they should be judged from our perspective. All humans struggle when doing science. It takes a lot of courage to write down and publish something new. In Figure 3.1, you can see the people that we will cover in the first part of the chapter. We will focus on findings in our solar system. How does everything work behind the curtain of nature? Many people have spent a long time thinking about it and have invented marvellous things like telescopes and advanced mathematics to enlighten humanity.
3.1 Models of the sun system
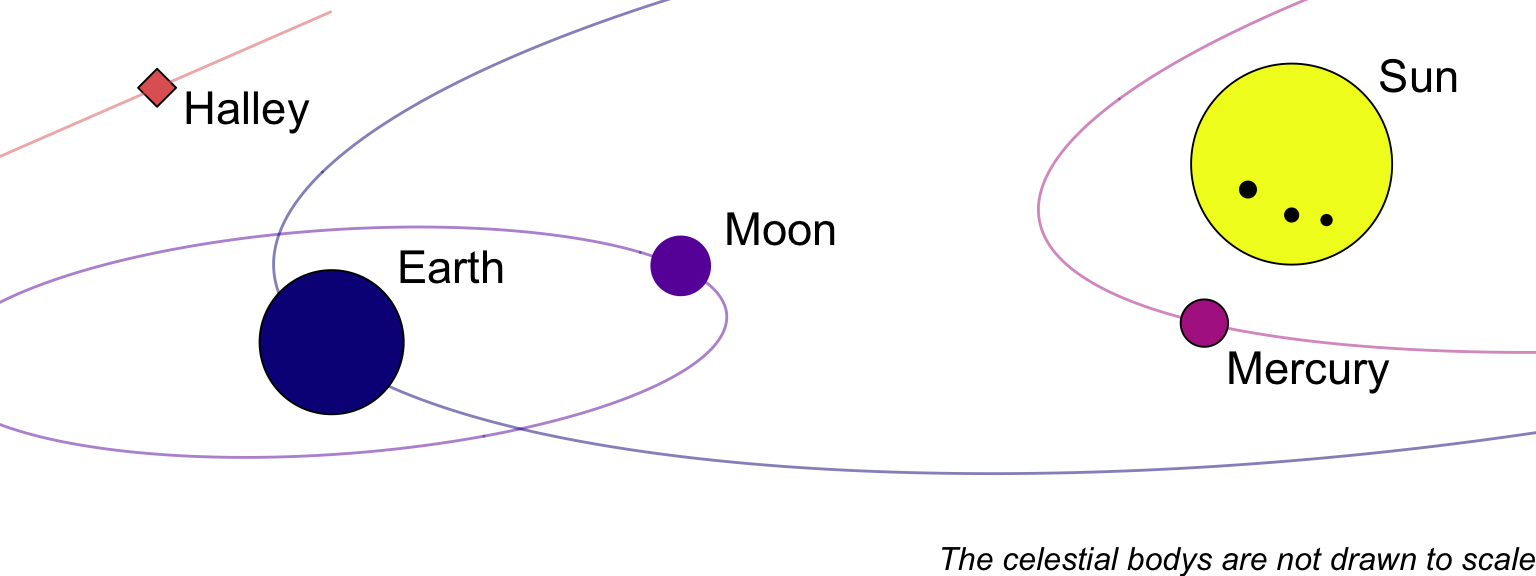
This chapter tries to tell the story of different men. It also explores their sins. And their misinterpretations of reality. All had brilliant ideas and promoted humanity for the better, and their actions showed great compassion and understanding. History repeats itself, so you can learn a lot from these men. Later in the book, we will focus on fleas and their characteristics. This simple life form is used as a model organism in our search for meaning in statistical models. In this chapter, we look to the stars. Humans stare into the black night and ask many questions about the workings of nature. How do plants move? What are the forces and orbits? It took centuries to answer these questions, with many scientists working without telescopes or modern mathematics. Moreover, modern mathematics was invented as a tool for searching the sky. In the following Figure 3.2, you will see celestial bodies that will be important in this chapter.
3.1.1 The hollow earth
Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) was born into a world that believed the Earth was at the centre of the universe. The people of his time believed in a geocentric worldview. In 1543, Nikolaus Kopernikus (1473–1543) proposed a heliocentric model of the universe, with the Sun at the center and the Earth orbiting it in a circular path. Nevertheless, the heliocentric worldview was still under debate when Kepler began his work. He studied the data observed by the astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546-1601). Brahe produced detailed observations of planetary movements. He made his observations without the use of a telescope. Brahe was meticulous about the accuracy of his measurements of planetary orbits, and was one of the first people to recognise the importance of making multiple observations. Brahe’s observations of Mars included the collection of all significant data on the planet’s position.
It was only on his deathbed that Brahe ordered Kepler to evaluate and publish his data. Kepler complied with this request. Until then, Brahe had rejected many of Kepler’s requests for access to the complete data tables. This is an early example of the importance of open data in research. Kepler found that the positional data for Mars deviated by eight arc minutes from the Copernican circular orbit. This small deviation led Kepler to propose elliptical orbits. Deviation is a key concept in science. To see a deviation and believe that it is a systematic one and not one of pure randomness or measurement error. We will come back to this again and again. Kepler believed in a systematic effect of the deviation and developed the three laws of planetary motion from there. This is also an early example of data acquisition and data science. Brahe produced the data, which Kepler then used data science to interpret.
You might now be wondering what an arcminute is. It is a unit of measurement for degrees. Therefore, one degree has 60 arc minutes, and one arc minute has 60 arc seconds. If you look at the full moon, you will see that it covers 32 arc minutes. Kepler therefore believed that the eight-arc-minute deviation in the orbit of Mars was a systematic failure of the 2,000-year-old theory, rather than an error in the measurements taken by its mentor, Tycho Brahe. Nevertheless, it took nearly two centuries of ongoing debate and research for Kepler’s work to take on its final, well-known form.
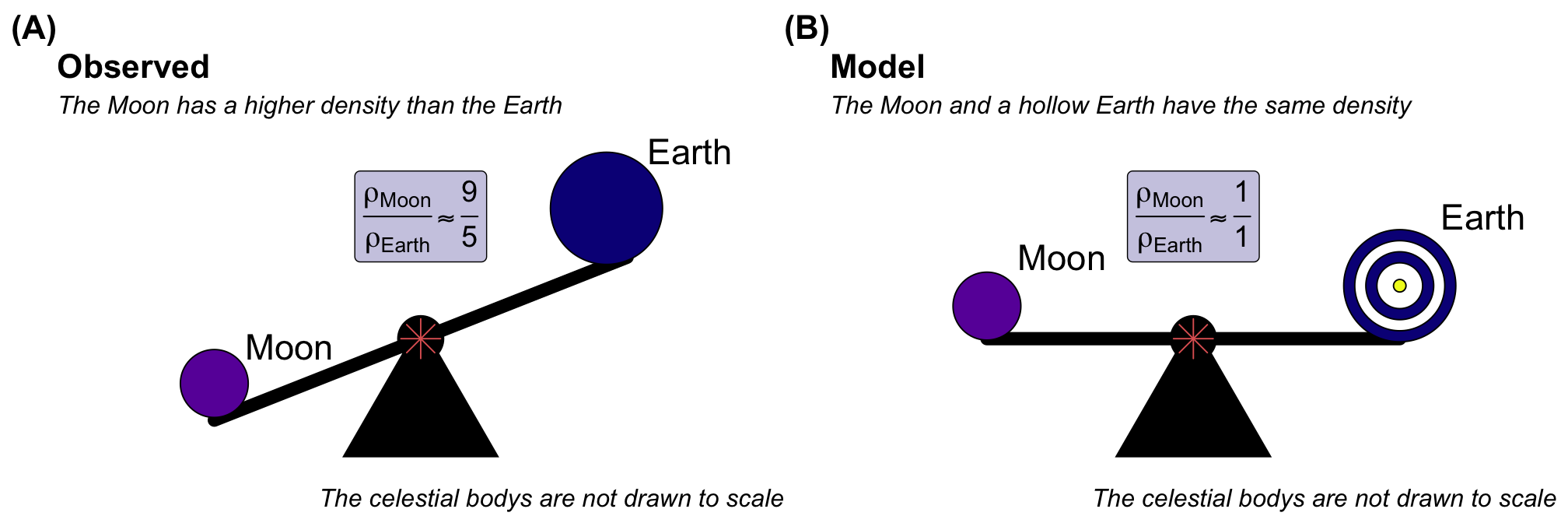
Following the discovery of elliptical orbits, Sir Isaac Newton (1643–1727) formulated the Newtonian theory of gravity. This new theory enabled humanity to calculate gravity on Earth, the Moon’s orbit around Earth, and the movement of the planets around the Sun. This is just one of many applications but not the first one. Edmond Halley (1656–1742) paid for the printing of Newton’s Principia, fascinated by the possibilities of Newton’s findings. Therefore he made one of the first usage of the formulas of Newton. Newton discovered that the Moon had a higher density than the Earth. Halley stated that the Moon and Earth are made of the same material. Therefore, the Earth could only be lighter if the Earth were hollow. However, Halley and Newton based their inaccurate density calculations on Newton’s theory of tides, which describes the movement of water in relation to the Moon’s mass and position. The calculations were wrong because they were based on false assumptions, resulting in an incorrect density ratio of \(9/5\) for the Moon and Earth.
From there on thinks start to escalate quickly. Halley deeply believed, that the earth is hollow. When 80-year-old Halley was portrayed as Astronomer Royal, he had himself depicted with a diagram of the hollow earth. The model was also used to describe the polar lights that come from the internal sun breaking through the Earth’s crust. Halley later became famous for being fortunate enough to correctly predict the return of Halley’s Comet. At the time, the prediction was considered a significant achievement of Newton’s theory of gravity. However, this success was a one-off, since Newton’s theory of gravity is incorrect, as we will discuss later. The idea of a hollow Earth did not disappear completely. In literature, the most famous public work is the book “Journey to the Centre of the Earth” by Jules Verne. The hollow earth theory lives on in many conspiracy theories to this day.
3.1.2 The habitable sun
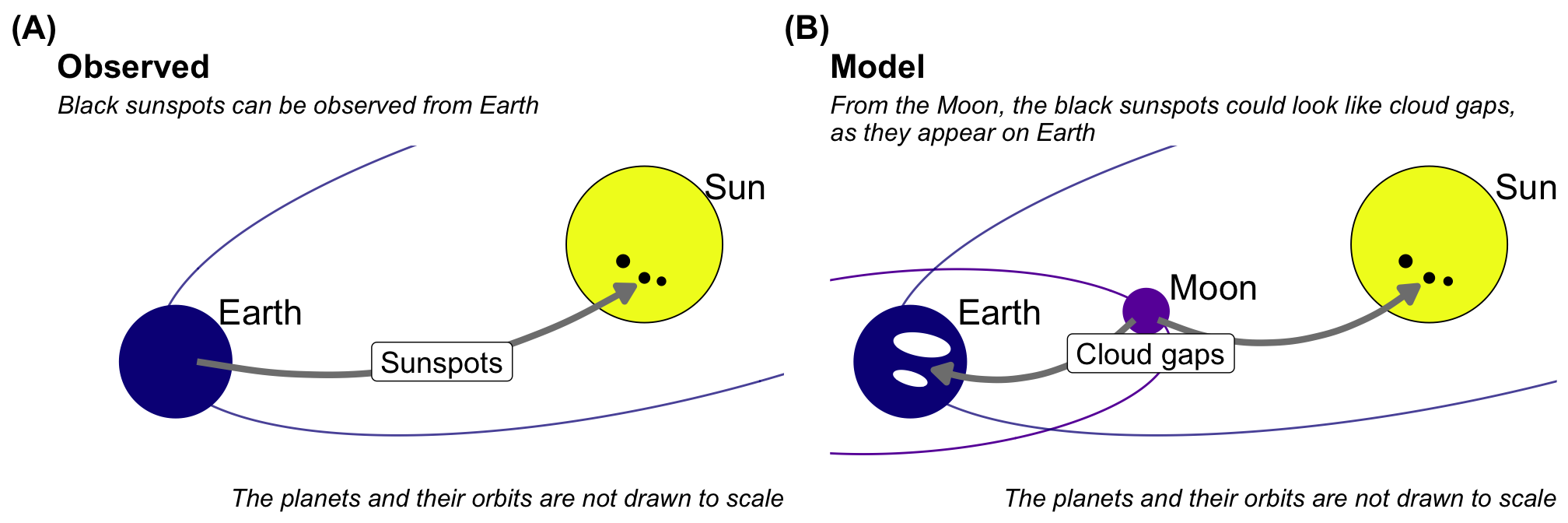
Our next example is about using a model with wrong assumptions to generate a theory of the habitable sun. For a modern reader, this sounds like an absolute joke, but in the time of Sir William Herschel (1738-1822), the idea was prominent. First, you must believe that everything has a purpose. Therefore, planets are meant to nurture life. Since there is life on Earth, every planet must have life. In other words, it is a human or anthropocentric world view. The sun is a planet. Why should the Sun be any different? The sun is a planet with luminous clouds. In addition, every planet is solid and has clouds.
Now, we are standing on Earth and looking at the Sun. What can we see? Small black spots, also known as sunspots. These cannot be observed with the naked eye — this should never be done — but can be seen with a telescope and appropriate filters. So, what are these sunspots? Herschel proposed the following model. Imagine standing on the moon and looking down at the Earth through the clouds. The Earth is a blue planet of water and land. The same is true of the Sun. You can see through the luminous clouds onto the dark surface of the solid sun. In the Figure 3.4, you can see the train of thought of Herschel.
Today4
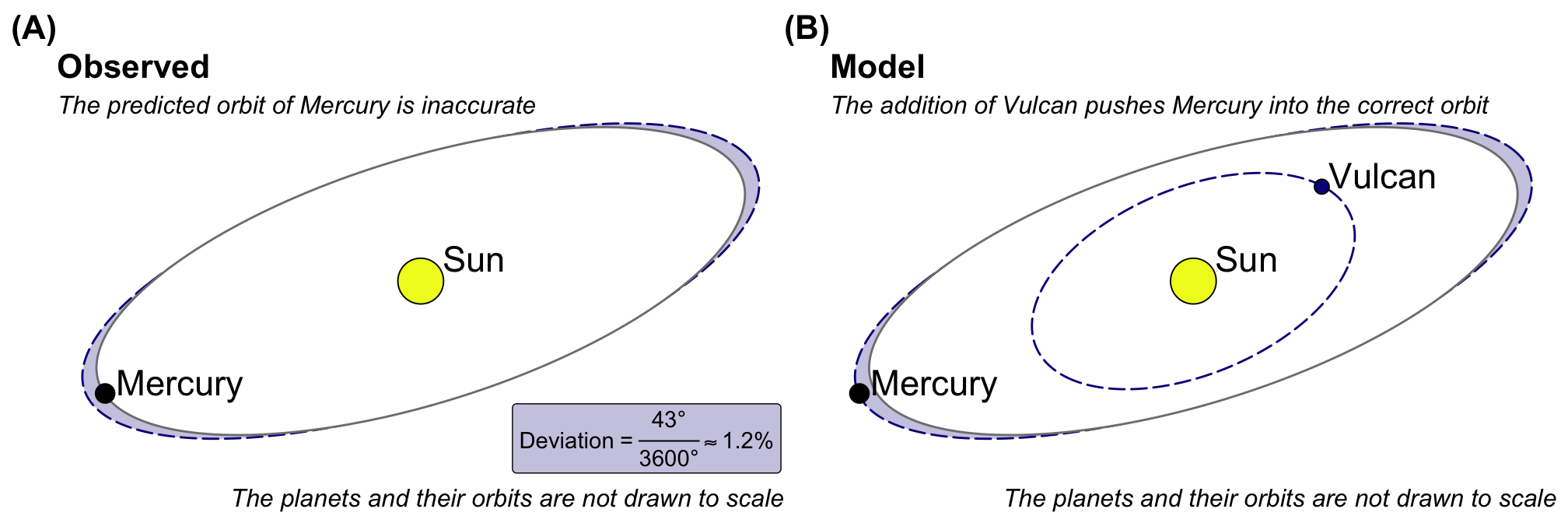
3.1.3 The planet Vulcan
Newton opened up a new field of classical physics. You might pause for a moment and ask yourself: if there is such a thing as classical physics, is there also modern physics? Yes and no. It depends on your perspective. Now, Newton became the benchmark for all new theories and models. Consequently, our observed data became increasingly detailed. We were able to determine the exact orbits of all planets. Everything seems to fit.
Problem solved. There was only one small deviation. The orbit of Mercury was slightly off. Specifically, the deviation was 43 arcseconds, or 1.2%, between the observed and calculated orbits using the Newtonian model. Albert Einstein (1879–1955) found this deviation intriguing. His General Theory of Relativity solved this mystery by merging time and space. Before Einstein’s theory was formulated, astronomers suggested the existence of a new planet. They suggested that the deviation would go away if a planet called Vulcan existed and circled the sun in a very narrow orbit. However, this planet was never found.
Always remember that models of reality can exist in parallel. Newton’s laws of gravity can be used, even though we know they are wrong and general relativity is less wrong. Why not, right? This is science. We can only reject a model if new observations do not fit into it. Then we must find a new, improved model. However, Newton’s laws are useful in everyday life when we are not moving near the speed of light or relatively to a large mass. In contrast, your GPS only works because we know the General Theory of Relativity. Without this theory, it would not be possible to build and use satellite navigation systems. You can choose your reality and the models you apply.
Still Einstein believed that the solar system was in the middle of the galaxy. And there were no more galaxies than the milky way.
Why is the nuclei so small? Considering quantum mechanics, we can only determine exactly the position or the momentum of an object. We see here momentum as speed. Therefore, if we know that the electron is near the nuclei, the speed must be very high. Therefore, the electron can not be very often near the nuclei. Hence, the electron does not fall into it. Due to quantum mechanics, the nuclei has to be so small to have a stable atom.
3.2 The difference between theory and model
Science is a process of guessing in the search for a good explanation.
If you can mathematically explain something, you can also mathematically predict something.
mathematically using a algorithm
A algorithm consists of mathematical formulas
A theory consists of models
A simple model can look like a mathematical formula
Theory models and formulas
Math and statistics, probabilistic worldview with quantum mechanics
Calculate versus estimate
What is a theory5
“Scientific knowledge, especially as stacked in textbooks, has an aura of objectivity - it is secure, uninfluenced by what we might hope or fear, and a solid assertion of what is true. Or, at least, that is what we are supposed to think. Knowledge, once formed, tends to become disembodied from its human origins. That is, while knowledge is preserved in the form of books, formulas, proofs, theorems, and such, we must not forget that before all this the formation of knowledge was the result of human thought, effort, and desire. Knowledge is a product of human hopes and fears; our emotions are crucial to its development, and its meaning cannot be truly understood if seen as some bloodless and emotionless enterprise.” — Joshua Schimel in Writing Science6
There are different types of models. In this book we will mainly talk about statistical models, which are a very specific type of mathematical models. There are other models. There are individual models, like models of control. The way in which we understand and experience reality. There are also scientific theories that can be read as umbrellas above a set of models. Theories and models can be viewed as forming a hierarchical structure. Theories are more general, whereas models are very specific. In everyday language, the terms ‘theory’ and ‘model’ are interchangeable.
As scientific workers, we work with models on a daily basis. Therefore, this book is about models. Although we may have a theory in the background, our daily life only sporadically touches such high levels.
Reality can be seen through science by carrying out tiny experiments. These experiments are tiny in the sense that reality is overwhelmingly big, so every experiment is tiny in comparison.
A model is a snapshot out of a bigger theory. Or to have another picture. A theory is a collage of different models. In each theory different models for a given problem exists. Hence, we can use different models in the Newotonian theory, like the formulas for the motion or gravity. Even if the formual ist wrong and a gravity force does not exists in reality.
3.3 Determinism in a probabilistic reality
“Nobody exists on purpose, nobody belongs anywhere, everybody’s gonna die. Come watch TV.” — Rick and Morty in Rixty Minutes
Atoms are the basic foundation of reality. Everything what is possible should be arise of the possibilities of atoms7.
Einstein don’t wanted to believe, that the old man is throwing dice in the alley until Officer Leroy comes up.
“Twistin’, shake it, shake it, shake it, shake it, baby; Hey, we gonna Loop de Loop Shake it out, baby; Hey, we gonna Loop de La” — The Blues Brothers (1980) – Shake a Tail Feather
3.4 Explanation vs. decision
Explanation and prediction are interchangeable. First, you need a model to explain something; then, you can use the model to make predictions.
Decision-making is slightly different. This could also be called a conclusion or, more technically, ‘inference’.
3.5 Alternatives
An Incomplete Theory: The Search for Quantum Gravity (a Story) by Megan Henry8
The The End of the Theory-Driven Era9
3.6 Glossary
- Theory
-
what does it mean.
- Model
-
what does it mean.
3.7 The meaning of “Models of Reality” in this chapter.
- Models of reality can exist in parallel.
- Models do not make automatically good predictions.
- If the assumptions are wrong, the model is wrong.